The Tesla Blueprint: Strategy, Success, and the Road Ahead
Exploring the Pillars of Tesla’s Growth and How It Stacks Up Against the Competition
Introduction
Tesla, Inc., founded by Elon Musk in 2003, has grown to become a leading player not only in the electric vehicle (EV) market but also in energy generation and storage. Tesla's vision to "accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy" drives its multi-faceted business strategy. This paper provides an in-depth analysis of Tesla's strategic pillars, financial performance, and competitive positioning, with detailed financial data and comparisons to key competitors: BYD, Ford, General Motors (GM), and Volkswagen (VW).
Tesla’s Business Model and Strategic Pillars
Product Innovation
Tesla’s commitment to product innovation is the cornerstone of its business strategy. The company continually invests in research and development (R&D) to push the boundaries of electric vehicle technology, battery efficiency, and autonomous driving.
R&D Investment: In Q1 2024, Tesla allocated approximately $1.25 billion to R&D, reflecting its commitment to maintaining its technological edge (Tesla, "Q1 2024 Earnings Call"). This is part of a broader strategy to enhance vehicle performance, reduce costs, and introduce new models such as the Cybertruck and the next-generation Roadster.
Battery Technology: Tesla's development of the 4680 battery cell is a significant innovation aimed at improving energy density, reducing production costs, and extending vehicle range. This innovation is crucial as battery efficiency directly impacts the overall cost and performance of electric vehicles. The company has already begun integrating these cells into its vehicles, with plans to scale production rapidly (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
Autonomous Driving: Tesla's Full Self-Driving (FSD) software remains at the forefront of autonomous vehicle technology. The company is continuously updating the software, with a focus on achieving Level 4 and eventually Level 5 autonomy. The deferred revenue related to FSD subscriptions was approximately $3.5 billion as of March 2024, highlighting the significant financial potential of this technology (Tesla, "Q1 2024 Earnings Call").
Vertical Integration
Tesla’s vertical integration strategy is designed to control every aspect of production, from battery manufacturing to vehicle assembly and software development.
Gigafactories: Tesla operates several Gigafactories worldwide, including in Nevada (USA), Shanghai (China), and Berlin (Germany). These factories are integral to Tesla’s ability to scale production and meet growing global demand. The Shanghai Gigafactory, for instance, contributed to a significant portion of Tesla's $21.3 billion in revenue in Q1 2024 (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
Supply Chain Control: Vertical integration allows Tesla to reduce dependency on third-party suppliers, which is critical in an industry where supply chain disruptions can have severe consequences. This strategy has also enabled Tesla to maintain high margins, with an automotive gross margin of 21.2% in Q1 2024 (Tesla, "Q1 2024 Earnings Call").
Global Expansion
Global expansion is a key element of Tesla’s growth strategy. The company has strategically established production facilities and sales networks in major markets around the world.
Revenue Distribution: Tesla's revenue is well-distributed across key markets. In Q1 2024, the company generated approximately $12 billion from the United States, $4.5 billion from China, and $3.8 billion from Europe, reflecting its strong global presence (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
New Markets: Tesla is actively exploring opportunities in emerging markets such as India and Southeast Asia. These markets represent significant growth potential due to increasing demand for sustainable transportation and supportive government policies. Tesla’s planned Gigafactory in India is expected to cater to both domestic and export markets, further solidifying its global footprint (Tesla, "HY 2024 Report").
Sustainability and Energy Independence
Tesla’s sustainability strategy extends beyond electric vehicles to include energy generation and storage solutions, which are becoming increasingly important as the world shifts towards renewable energy.
Energy Division Performance: Tesla's energy division, which includes products like Powerwall, Powerpack, and Megapack, generated $1.6 billion in revenue in Q1 2024, representing a year-over-year growth of 40% (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report"). This growth is driven by increasing demand for energy storage solutions from both residential and commercial customers.
Solar Products: Tesla’s solar energy products, including the Solar Roof, are integral to its vision of creating a sustainable energy ecosystem. While the solar division currently represents a smaller portion of total revenue, it is expected to grow significantly as adoption increases. The gross margin for the energy generation and storage segment improved to 22% in Q1 2024, reflecting operational efficiencies and economies of scale (Tesla, "Q1 2024 Earnings Call").
AI and Autonomous Driving
Tesla’s advancements in AI and autonomous driving technology are key differentiators in the automotive industry.
Full Self-Driving (FSD): Tesla’s FSD software continues to evolve, with the company aiming to achieve full autonomy in the near future. As of Q1 2024, over 400,000 Tesla vehicles were equipped with FSD, generating substantial recurring revenue through software subscriptions (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
Optimus Robot: Beyond vehicles, Tesla is exploring AI applications in other areas, such as the Optimus robot. This humanoid robot is designed to perform tasks that are dangerous or repetitive, potentially opening up new markets for Tesla in industrial and domestic robotics. The company’s investment in AI R&D is expected to exceed $1 billion annually by 2025 as it expands its AI capabilities (Tesla, "Q2 2024 Earnings Call").
Tesla SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Market Leadership in EVs: Tesla is the dominant player in the electric vehicle market, with strong brand recognition and a significant share of the global EV market.
Technological Innovation: Tesla leads in several key areas such as battery technology (e.g., 4680 cells), autonomous driving (Full Self-Driving or FSD), and over-the-air software updates.
Vertical Integration: Tesla’s control over the supply chain, including in-house battery production, software development, and vehicle manufacturing, allows for higher margins and rapid innovation.
Global Manufacturing Footprint: Tesla’s Gigafactories in the U.S., China, and Europe enable it to meet growing global demand while reducing logistics costs and tariff exposure.
Sustainability Leadership: Tesla’s focus on renewable energy, through its energy storage products (Powerwall, Powerpack, Megapack) and solar solutions, positions it as a leader in the transition to sustainable energy.
Weaknesses
High Capital Expenditure: Tesla’s strategy of vertical integration and rapid expansion requires significant capital investment, which can strain cash flow and impact profitability.
Reliance on a Limited Product Line: Tesla’s current vehicle lineup is relatively limited compared to traditional automakers. This focus on a few models could limit market appeal in other segments.
Quality Control Issues: Tesla has faced criticism for quality control, particularly in the early stages of production for new models. These issues can harm the brand’s reputation, especially as competition increases.
High Price Sensitivity: Tesla’s vehicles are priced at a premium, which makes them vulnerable to economic downturns or shifts in consumer spending. Price cuts, while boosting sales, can erode margins and brand perception.
Supply Chain and Production Bottlenecks: Tesla’s vertical integration means it is highly dependent on its own production capabilities, making any internal disruptions significantly impactful.
Opportunities
Expansion into New Markets: Tesla has significant opportunities to expand into new geographic markets, such as India and Southeast Asia, where EV adoption is still in its early stages.
New Product Launches: Upcoming models like the Cybertruck and Roadster, as well as the potential development of a more affordable vehicle, represent significant growth opportunities.
Advancements in Autonomous Driving: Tesla’s continued development of Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology presents a major opportunity, potentially leading to new revenue streams from software subscriptions and licensing.
Energy Storage and Solar Growth: The global transition to renewable energy creates a vast market for Tesla’s energy storage and solar products, potentially driving significant revenue growth.
AI and Robotics: Tesla’s investments in AI, particularly with the development of the Optimus robot, open up entirely new business opportunities beyond the automotive sector.
Threats
Intensifying Competition: Traditional automakers like Ford, GM, and Volkswagen are rapidly expanding their EV portfolios, while new entrants like BYD are challenging Tesla’s dominance, particularly in China.
Regulatory Risks: Tesla operates in a highly regulated industry, and changes in environmental, safety, or trade policies could impact its operations.
Economic Downturns: Tesla’s premium pricing makes it vulnerable to economic downturns, where consumers may prioritize cost over innovation.
Supply Chain Disruptions: While Tesla’s vertical integration reduces dependency on external suppliers, it also makes any internal disruptions significantly impactful.
Technological Risks: The rapid pace of technological change in the automotive and energy industries poses a constant threat, particularly if competitors develop superior technology or if Tesla fails to deliver on its ambitious goals.
Financial Performance
Tesla’s financial performance is a reflection of its effective execution of strategic initiatives. The company has consistently reported strong revenue growth, driven by robust demand for its vehicles and energy products, as well as improving operational efficiency.
Revenue, Costs, and Profitability
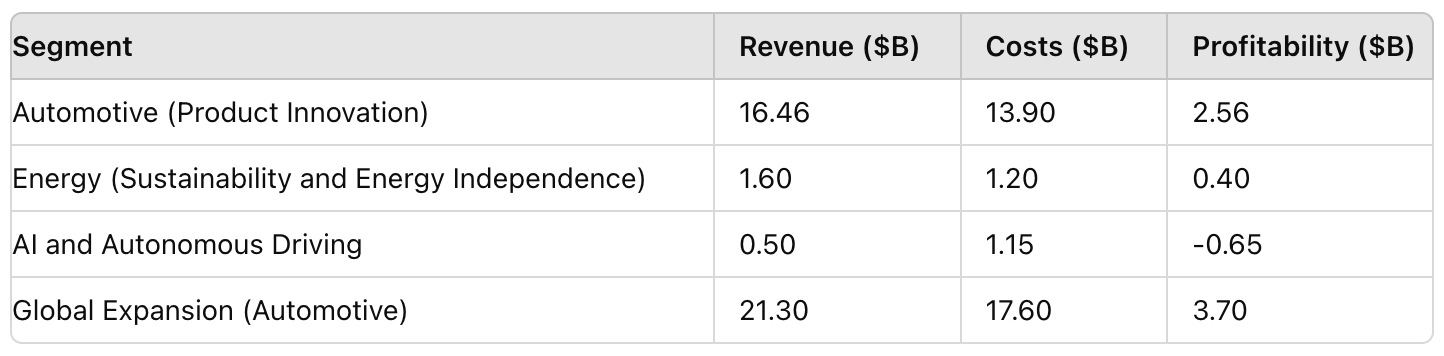
In Q1 2024, Tesla reported total revenue of $23.33 billion, a 35% increase year-over-year. The automotive segment remains the largest contributor, generating $16.46 billion in revenue. The energy generation and storage segment contributed $1.6 billion, while the AI and autonomous driving segment, though smaller, is rapidly growing.
Gross Margin: Tesla’s overall gross margin for Q1 2024 was 21.2%, slightly lower than the previous quarter due to increased raw material costs and investments in new technologies. However, Tesla’s vertical integration and scale efficiencies helped maintain relatively high margins compared to industry peers (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
Operating Costs: Operating expenses totaled $2.4 billion in Q1 2024, with R&D accounting for $1.25 billion and SG&A (selling, general, and administrative) expenses at $1.15 billion. Despite these high expenditures, Tesla achieved an operating margin of 11.8%, demonstrating effective cost management (Tesla, "Q1 2024 Earnings Call").
Net Income: Tesla reported a net income of $2.56 billion for Q1 2024, up from $1.96 billion in the same quarter of the previous year. This increase was primarily driven by higher vehicle deliveries, FSD subscriptions, and improved cost efficiencies (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
Chart 1: Tesla’s Revenue, Costs, and Profitability by Segment (Q1 2024)
Here is the chart that provides a clear visual representation of Tesla’s financial performance by segment in Q1 2024:
Competitive Analysis
Tesla operates in a highly competitive market, facing challenges from both traditional automakers and emerging EV companies. Below is a detailed competitive analysis comparing Tesla to its key competitors: BYD, Ford, GM, and Volkswagen.
Market Position
Tesla: Tesla remains the global leader in electric vehicles by market share, particularly in premium segments. Tesla’s brand is closely associated with innovation, sustainability, and advanced technology, making it the benchmark for EVs worldwide.
BYD: BYD is the largest EV manufacturer in China and has overtaken Tesla in EV sales within the Chinese market. BYD’s strength lies in its broad product lineup, which covers various price segments, from affordable EVs to luxury models. The company benefits from strong government support and a deep understanding of the domestic market (BYD, "2024 Financial Report").
Ford: Ford is an established player in the global automotive market, with a strong presence in North America. The company has been rapidly expanding its EV offerings with models like the Mustang Mach-E and the F-150 Lightning, though it still lags Tesla in overall EV market share and brand perception in the EV segment (Ford, "Q2 2024 Earnings Call").
GM: GM is one of the largest automakers in the world, with a diverse vehicle lineup. GM has committed to an all-electric future and is making significant investments in EVs, including the Ultium battery platform. However, GM’s EV market share is still growing, and it remains behind Tesla and BYD in global EV sales (GM, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
Volkswagen (VW): VW is a major global automaker and one of Tesla’s most formidable competitors in Europe. The company has made a significant push into the EV market with its ID. series, which has been well-received in Europe. VW’s scale and global reach make it a strong competitor, though it still trails Tesla in terms of brand strength in the EV sector (Volkswagen, "Q2 2024 Financial Report").
Innovation and Technology
Tesla: Tesla leads the industry in innovation, particularly in autonomous driving, battery technology, and software integration. Tesla’s proprietary technologies, such as the Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and the 4680 battery cells, give it a significant competitive edge. The company’s ability to roll out over-the-air updates to enhance vehicle performance and safety further cements its position as a technology leader (Tesla, "Q1 2024 Earnings Call").
BYD: BYD is a leader in battery technology, particularly with its Blade Battery, which is known for its safety and durability. While BYD excels in battery manufacturing, it lags behind Tesla in autonomous driving technology and global software capabilities. BYD focuses heavily on vehicle electrification and battery production, leveraging its expertise to maintain competitive pricing (BYD, "2024 Financial Report").
Ford: Ford has been innovative with its EV offerings, such as the Mustang Mach-E and F-150 Lightning, which have garnered significant market attention. However, Ford’s autonomous driving technology, BlueCruise, is less advanced compared to Tesla’s FSD. Ford is focusing on integrating its vehicles with connected services but remains behind Tesla in overall technological leadership (Ford, "Q2 2024 Earnings Call").
GM: GM’s innovation is centered around its Ultium battery platform, which supports a wide range of EVs. GM’s Super Cruise is a competitive semi-autonomous driving feature, but it is not as advanced as Tesla’s FSD. GM is investing heavily in EVs and autonomous technology, though widespread deployment and consumer adoption are still in the early stages compared to Tesla (GM, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
Volkswagen (VW): VW has focused on modular electric platforms (MEB) that support a wide range of EVs across different brands. VW is also investing in autonomous driving, but like Ford and GM, it is behind Tesla in this area. VW’s strength lies in its engineering and mass production capabilities, particularly in Europe (Volkswagen, "Q2 2024 Financial Report").
Financial Performance
Tesla: Tesla’s financial performance is robust, with high margins and consistent revenue growth. In Q1 2024, Tesla reported total revenue of $23.33 billion, with a gross margin of 21.2% and an operating margin of 11.8%. Tesla’s profitability is driven by strong demand for its vehicles and energy products, as well as operational efficiencies achieved through vertical integration (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
BYD: BYD has shown impressive financial growth, particularly in its EV segment, with revenues surpassing Tesla’s in the Chinese market. In the first half of 2024, BYD reported revenues of approximately $30 billion, driven by its expansive product lineup and lower production costs. However, BYD’s margins are lower than Tesla’s, partly due to its broader product lineup, which includes lower-margin vehicles (BYD, "2024 Financial Report").
Ford: Ford’s financials reflect a traditional automaker transitioning to EVs. While Ford has strong revenues from its legacy business, its EV segment (Model e) has been operating at a loss, primarily due to significant investments in new technology and production capacity. Ford reported a total revenue of $45 billion in Q2 2024, but its EV segment contributed to an operating loss of $700 million (Ford, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
GM: GM remains profitable, but like Ford, its EV segment is currently a drag on earnings as the company ramps up production and invests in new technology. GM reported revenues of $39 billion in Q2 2024, with an overall gross margin of 15%, but its EV segment is still in the investment phase, impacting short-term profitability (GM, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
Volkswagen (VW): VW has strong revenues and a solid financial foundation, driven by its global sales and diverse product lineup. VW reported revenues of €70 billion in Q2 2024, with a gross margin of 19%. VW’s heavy investment in EVs has impacted short-term profitability, but the company remains one of the most financially robust competitors to Tesla, particularly in Europe (Volkswagen, "Q2 2024 Financial Report”).
Global Expansion
Tesla: Tesla’s global expansion strategy is robust, with Gigafactories in the U.S., China, and Europe, and plans for further expansion in emerging markets like India and Southeast Asia. Tesla’s ability to scale production globally gives it a significant advantage, particularly in meeting local demand and reducing logistics costs. In Q1 2024, Tesla’s international operations contributed approximately $8.3 billion to total revenue (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
BYD: BYD’s strength lies in China, but it is rapidly expanding its presence in other markets, including Europe, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. BYD’s strategy includes launching new models tailored to local markets and expanding its global manufacturing footprint. In 2024, BYD announced plans to build a manufacturing facility in Europe to cater to the growing demand for EVs in the region (BYD, "2024 Financial Report").
Ford: Ford’s global expansion is focused on North America and Europe, with a growing presence in China. Ford is expanding its EV production capabilities but remains less globalized in its EV business compared to Tesla and VW. Ford’s international operations accounted for approximately 40% of its total revenue in Q2 2024, highlighting its strong presence outside the U.S. (Ford, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
GM: GM’s global presence is significant, particularly in North America and China. GM is expanding its EV operations globally, with a focus on the U.S. and China, but its EV production is still catching up with Tesla and BYD in scale. GM’s international operations contributed approximately $14 billion to its total revenue in Q2 2024 (GM, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
Volkswagen (VW): VW has a strong global presence, particularly in Europe, China, and South America. VW’s global scale is comparable to Tesla’s, and it is rapidly expanding its EV production capacity, especially in Europe and China. VW’s international operations generated approximately 80% of its total revenue in Q2 2024, making it one of the most globally diversified automakers (Volkswagen, "Q2 2024 Financial Report").
Sustainability and Energy
Tesla: Tesla’s comprehensive approach to sustainability, integrating energy solutions with EVs, sets it apart from competitors. Tesla’s energy division generated $1.6 billion in revenue in Q1 2024, reflecting its commitment to renewable energy. Tesla’s solar and energy storage products are designed to work seamlessly with its vehicles, providing a complete sustainable energy ecosystem for consumers (Tesla, "Q1 2024 10-Q Report").
BYD: BYD is heavily involved in battery production and energy storage solutions, primarily focused on the Chinese market. While BYD’s sustainability efforts are centered around electrification and reducing emissions, it does not have the same level of integration between vehicles and energy products as Tesla. However, BYD’s extensive battery production capabilities give it a competitive edge in the renewable energy market (BYD, "2024 Financial Report").
Ford: Ford’s sustainability efforts are centered around electrification and reducing emissions. Ford does not have a significant presence in the energy sector, which limits its ability to offer a comprehensive sustainability solution like Tesla. Ford’s focus is on producing more fuel-efficient vehicles and transitioning to EVs, with a goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 (Ford, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
GM: GM is focusing on electrification and plans to become carbon neutral by 2040. GM is investing in renewable energy for its operations but lacks the integrated energy product line that Tesla offers. GM’s sustainability strategy is primarily driven by its commitment to reducing emissions through the widespread adoption of EVs (GM, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
Volkswagen (VW): VW is committed to reducing emissions and has a strong focus on sustainability through its EV offerings. VW is investing in renewable energy for its operations and offers some energy solutions, but it does not match Tesla’s integrated approach to vehicles and energy. VW’s sustainability efforts are also supported by its modular electric platforms, which reduce the environmental impact of vehicle production (Volkswagen, "2024 Sustainability Report").
AI and Autonomous Driving
Tesla: Tesla is a leader in AI and autonomous driving with its Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology. Tesla’s continuous development of FSD and other AI-driven products like the Optimus robot sets it apart from most competitors. Tesla’s AI capabilities are a key differentiator in the EV market, and its investments in AI R&D are expected to exceed $1 billion annually by 2025 (Tesla, "Q2 2024 Earnings Call").
BYD: BYD has made progress in autonomous driving but is behind Tesla in terms of both technology and deployment. BYD focuses more on vehicle electrification and battery technology than on AI and autonomous driving. The company is investing in AI, but its autonomous driving technology is still in the early stages compared to Tesla’s advanced capabilities (BYD, "2024 Financial Report").
Ford: Ford’s autonomous driving technology, BlueCruise, is less advanced than Tesla’s FSD. Ford is investing in AI and connected vehicle services but remains behind Tesla in overall AI capabilities. Ford’s focus is primarily on enhancing driver-assist features and ensuring safety, rather than achieving full autonomy in the near term (Ford, "Q2 2024 Earnings Call").
GM: GM’s Super Cruise is a competitive semi-autonomous driving feature that offers hands-free driving on certain highways. However, it is limited compared to Tesla’s FSD, which aims for full autonomy. GM is heavily investing in its autonomous subsidiary, Cruise, which focuses on developing fully autonomous vehicles for urban environments. Despite these investments, GM’s autonomous technology is still in the testing and early deployment stages (GM, "Q2 2024 10-Q Report").
Volkswagen (VW): VW is developing autonomous driving technology as part of its broader push into EVs and digital services. However, like Ford and GM, VW is behind Tesla in terms of both software development and deployment of autonomous features. VW’s current focus is on improving driver-assistance systems, with full autonomy seen as a longer-term goal. The company is investing in AI and autonomous driving through partnerships and internal R&D, but it has not yet achieved the same level of technological maturity as Tesla (Volkswagen, "2024 Sustainability Report").
Conclusion
Tesla’s strategic approach is characterized by its focus on innovation, vertical integration, global expansion, sustainability, and AI. The company’s ability to innovate rapidly, scale production globally, and integrate renewable energy solutions with its vehicles has positioned it as a leader in both the automotive and energy sectors. Despite facing intense competition from both traditional automakers and emerging EV companies, Tesla’s strong brand, technological leadership, and effective execution of strategic initiatives give it a competitive edge.
Tesla’s financial performance reflects the success of its strategy, with consistent revenue growth, high margins, and robust profitability. The company’s aggressive investments in R&D and global expansion have positioned it well for future growth, particularly as the global transition to electric vehicles and renewable energy accelerates.
However, Tesla’s competitors are not standing still. Companies like BYD, Ford, GM, and Volkswagen are making significant strides in EV technology, global expansion, and sustainability. While Tesla currently leads in many areas, the competitive landscape is evolving rapidly, and maintaining its leadership position will require continued innovation and strategic agility.
References
Tesla, Inc. "Q1 2024 Earnings Call Transcript." Seeking Alpha, 2024, https://seekingalpha.com/symbol/TSLA/earnings.
Tesla, Inc. "Q1 2024 10-Q Report." SEC Filings, 2024, https://www.sec.gov/edgar/browse/?CIK=1318605&owner=exclude.
Tesla, Inc. "Q2 2024 Earnings Call Transcript." Seeking Alpha, 2024, https://seekingalpha.com/symbol/TSLA/earnings.
Tesla, Inc. "HY 2024 Earnings Report." Tesla Investor Relations, 2024, https://ir.tesla.com/.
BYD Company Ltd. "2024 Financial Report." BYD Investor Relations, 2024, http://www.byd.com/en/Investor.html.
Ford Motor Company. "Q2 2024 Earnings Call Transcript." Seeking Alpha, 2024, https://seekingalpha.com/symbol/F/earnings.
General Motors. "Q2 2024 10-Q Report." SEC Filings, 2024, https://www.sec.gov/edgar/browse/?CIK=1467858&owner=exclude.
Volkswagen AG. "Q2 2024 Financial Report." Volkswagen Investor Relations, 2024, https://www.volkswagenag.com/en/InvestorRelations.html.
Volkswagen AG. "2024 Sustainability Report." Volkswagen Investor Relations, 2024, https://www.volkswagenag.com/en/InvestorRelations.html.